Covered Call – Neutral Option Trading Strategy suitable for beginners
Last Updated Date: Nov 16, 2022A covered call is a financial transaction in which the investor who sells the call options owns the same amount of the underlying security.
To begin with, the investor holding a long position in an asset writes or sells call options on the very same asset to generate income.
The ‘cover’ suggests that the seller can transfer the shares if the buyer of the call option wants to purchase.
It is basically a neutral strategy where the investors only expect a minimal increase or decrease in the underlying stock. It is for the life of the call option in place.
Understanding Covered Call Option Strategy
The investor views the option plan as a short-term neutral underlying stock. For this, the reason he holds the asset longer and simultaneously has a short option. It happens is generating income in the form of an option premium.
Simply said, if the investor wants to hold the asset for the long term, he can work on premium. He may not see any appreciable increase in the price shortly.
Now, they can generate income in premium while the stock is in possession. It serves as the short term hedge for the investors to earn income via premium for selling the option.
However, the investor even has to forfeit the stock gains if the price moves above the strike price. Here, strike price is the price at which the option holder purchases the call option.
It is neither very useful for the bearish investor nor a very bullish investor. If an investor has a very bullish type then, it will be better off for him to hold the stock and not write the option. If the stock price hikes, then the overall profit of the investor might reduce if he sells earlier.
Similarly, if an investor is of the very bearish kind, then they may simply sell off their stock as, when the stock hikes then, the premium received for writing the call option would be quite less to offset the loss on the stock.
Open a Demat Account Now! – Apply this Options Strategy
Why use the Covered Call Options Trading Strategy?
The covered call is basically one of the options trading strategies, as normally, derivates are a profit-making stock or tool.
However, this strategy isn’t to make a profit from the options. It is primarily to return a profit from the stock that goes through the neutral stage of neither increase in price nor any decrease.
If the perspective of seeing the stock is neutral then one would use it but don’t sell it and would prefer to make some profit without moving.
One may even use to reduce losses if the price of the stock falls. If someone is looking for any protection against a sizable fall then the protective put is a better choice.
Establishing the Covered Call Neutral Trading Strategy
One can create a covered contract right from scratch. One can buy the required stocks initially and then write a particular option contract.
However, cover contracts are what we widely use when we have purchased it. And having a neutral strategy for the option stock, one would probably have better strategies to use.
Establishing a cover call might be very achievable and simple. Firstly, we have to make sure of enough calls. That is using the sell to open order, in order to cover the number of shares a person owns.
Then secondly, it has to be there at a strike price which is generally above the current price. The trader usually states the price to be above the current price of the shares.
When the options are written at a higher strike price, then one makes a higher return if the prices of the stock increase, but if the price remains the same then less income is made. One will also have less protection should it fall.
Find out other Neutral Option Trading Strategy here
| Calendar Straddle | Covered Put | Short Straddle |
| Iron Condor Spread | Short Strangle | Call Ratio Spread |
| Butterfly Spread | Albatross Spread |
Choosing an Expiration Date
While choosing an expiration date for the options, one should choose the expiration that is the closest, namely the nearest month.
By exercising this, one will benefit a quick rate of time decay. There is a shorter time span for the stock to move at price.
An example of the covered call can be: one has 100 shares of company A stocks which are currently at Rs.50. This price can be the starting point.
We believe that the price won’t move over the next few weeks. We can see it as an opportunity to profit from it.
Out of the money calls with the strike price of Rs.52, the expiration date that seems to be closest is trading at Rs.1.
So the person will write one call option contract in which each contract contains 10 options and then receive a credit of Rs.100.
Profiting from this Covered Call Options Strategy
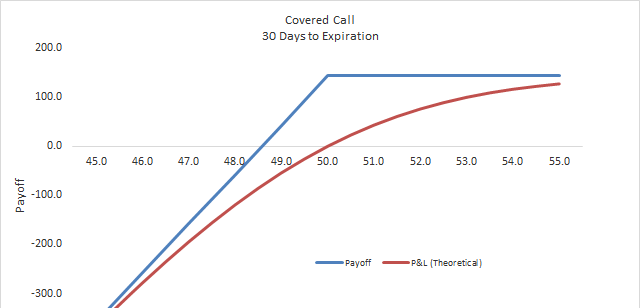
We can expect the maximum profit when the price of the shares increases to the strike price of the options written at the time of the expiration. This would come true in the above example when company A will be trading at Rs.52.
As this situation arrives, the options would expire worthlessly. Now, the credit received can remain, whereas we don’t have to expect any further obligation.
Therefore, the profit would be Rs.100. One would also profit from the shares that they have by increasing in value.
In the case above, a profit of Rs.200 is what we can expect by multiplying 100 shares with Rs.2 per share. Now the total profit would be Rs.300.
The return of profit on the covered call is even received if the price won’t move at all and also if the increase is to a price lower than the strike price of the option contract written.
Again, the calls that are written would expire worthlessly and the credit will be kept as a profit. So the profit potential of the strategy can be summarized as:
- When the price of the underlying stocks is equal to the strike price of the option contract, then the maximum profit is made.
- Profit can also be made when the price of the underlying stock is greater than or equal to the starting point but less than the strike price of the option contract.
- The profit per share or the profit of the option written is the difference in the price of the underlying stock and the starting point and adding up to that is the price per option.
- Lastly, the profit is not applicable when the price of the underlying stock is greater than the strike price of the option contract.
Find out more relevant Neutral Option Trading Strategy below
| Condor Spread | Calendar Put Spread | Iron Albatross Spread |
| Calendar Call Spread | Short Gut | Covered Call Collar |
| Put Ratio Spread | Iron Butterfly Spread | Calendar Strangle |
Potential Risks of Covered Call Strategy
One has to take care of two main risks using the strategy. Firstly, if the stock falls in value, it provides very little protection.
Any loss one incurs from the drop in the value of the stock will have its compensation. It happens only by the credit which happens in writing the options contract.
In the example above, when the price falls to $49 then the loss seems to get covered. If the price falls below Rs.49 then there would be no additional returns from the stock. Shares won’t fall in price significantly though which has to be kept in mind always.
As we can argue that one would incur any losses only by owning the loss. Now, the covered cost at least gives some return to the investor.
But one has to take care of the fact that it isn’t a suitable strategy to think like that. The share prices may or may not drop significantly in value.
More Risks Associated with Covered Call
The second main risk is that one is not going to make any further profit if the stock price rises above the strike price of the options written.
In the above example, if the price of the stock rises above Rs.52, then we could assign the call. Now, the person will have to sell his stock at the strike price of Rs.52.
Although this doesn’t mean that we cannot find a profit, it still happens if we hold the stock for long. It is possible we have more profit rather than applying to the covered call.
So lastly, a covered call is a simplified strategy which is great if one owns stock that is going to be relatively stable in price over a period of time.
The applying stage does not demand much of a cost. Now, we can generate returns easily and effectively without moving at the price.
The only cons with it are that the covered call can limit one’s profit when the price of the stock goes unexpectedly high and it offers no actual protection when it goes down.
Open a Demat Account Now! – Apply this Options Strategy
Similar Topics on Options Trading
