Economies of Scale – Concept, Basics, Beneficiary, Types, Impact & more
Last Updated Date: Sep 01, 2023One can achieve economies of scale when more units of goods or services are produced on a large scale having the minimum production cost.
In simple terms, One can say that an organization is growing by increasing production and decreasing costs.
As per this theory, experts say that a company can achieve economies of scale.
What are economies of scale?
When the increasing scale of production aligns with the decreasing average cost, one can achieve the economies of scale.
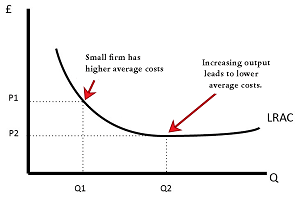 In simple terms, the cost of production decreases when a company starts producing more quantity of products.
In simple terms, the cost of production decreases when a company starts producing more quantity of products.
It is mainly because the fixed costs, including administration, rent, etc., are distributed among different production units.
Under some conditions, companies can achieve economies of scale by reducing average variable costs. The best part about economies of scale is that it minimizes the price per unit.
It is crucial in the real world because when companies grow in size, they can indeed become more efficient.
In some cases, a business cannot be profitable or efficient if they fail to have economies of scale. On the flip side, in some industries, it must be enormous if the company wants to strive.
You can also say that economies of scale are ideally cost advantages that a company reaps when they start producing efficiently.
Companies can quickly achieve economies of scale by enhancing production.
When we talk about economies, the company’s size matters significantly as the larger the size of the company, the more it can save.
Open Demat Account Now! – Zero Brokerage on Delivery
Economies of Scale – Basics & History
Long back, a famous economist, Adam Smith, identified two main divisions for achieving a better production on sale, including labor and specialization.
The best part about these techniques is employees can indeed concentrate on some particular tasks and enhance the skills they need for better performance.
Above all, if one has efficiency, they can save both time and money while boosting the production capacity of their business.
No matter what business one owns, one thing is for sure that economies of scale are quite vital.
It is because it highlights the competitive advantage and cost savings that the giant companies have over small firms.
The majority of the customers fail to understand the reason behind why a small company charges more for the same product which a small company sells.
It is mainly because the cost per unit depends mostly on the production by the company.
Above all, the large companies produce more goods by spreading the production cost over another amount of goods.
If there are a plethora of companies making the same goods in one industry, then the drive is most likely to dominate the product’s cost.
There are many reasons why economies of scale tend to leads to minimum cost per unit. Both labor specialization and integrated technology tend to increase production volumes.
Additionally, the lower price of products stems from wholesale orders, advertising buys, or lower cost of capital.
Lastly, the cost of the product also decreases when internal functioning is spread over to more units. Some of the internal functions include accounting, information technology, and marketing.
The first reasons can be operational efficiencies and synergies, while the secondary reasons can be mergers and acquisitions.
Beneficiaries of Economies of Scale
No doubt, economies of scale are often known as benefits of businesses because they increase the sale.
But at the same time, other parties can also benefit from economies of scale by increasing their efficiency and productivity. These include governments, non-profits, and individuals.
You can say any party can achieve economies of scale as long as they reduce the average cost. Any government, individual or non – profit organization can have a competitive advantage over others.
In simple terms, you can say that the quality of goods and services are of better quality as compared to the competitors. More the size of the business lower will be the cost.
Whenever possible, individuals can also experience economies of scale if they make a bulk purchase, as buying bulk minimizes the cost per unit to the consumer.
It happens mainly because the seller has to do less packaging and spend a minimum amount on it. Also, consumers can save money as they don’t need to go from one retailer to another.
Specialization and Division of Labor
The father of economics, Adam Smith, back in the 18th century, wrote about specialization and division of labor regarding the scope of economies.
As per Smith, there are two main returns on production and specialization and division of labor. By using these strategies, people can focus on expert tasks and become better at their work.
Over time, all the tasks are performed at a greater level of quality and skill besides a higher rate.
It allows the companies to increase their profits due to specialization and division of labor minimize the time and money which is required for production. It helps in increasing the overall output.
Types of Economies of Scale
Here are the various types of Economies of Scale –
Internal Economies of Scale
It is all about economies that are unique to a company. For example, a company may hold a company over mass production.
It allows the company to minimize the average cost of production as compared to other firms operating in the industry.
Internal economies of scale cut cost by increasing their levels of production. Examples of internal economies:
Technology – A large company can quickly adapt production technologies of production which a small-cap company can’t afford.
It is because larger companies have a lot of capital to invest in expensive things especially in machinery form.
The cost of manufacturing decreases at least 70 to 80 percent every time a company increases its production. It is mainly because you have access to better quality equipment.
Bulk buying power – If a company has the greater buying power, a large firm can buy its factor input in bulk at discounted costs.
You can also refer to it as monopsony power. The company buys more from suppliers at a lower price, so the price per unit decreases.
Finance – Large companies are most likely to be more credit-worthy because they have fantastic access to credit. It is all because of favorable rates of borrowing.
Additionally, they have excellent financing options at lower interest rates. In simple terms, they can access the capital at relatively cheaper options.
Network – One can commonly find the network of economies of scale, mainly in online business. Under this type of network, each added firm doesn’t necessarily add any additional cost virtually.
In simple terms, adding more customers can increase the scale of the company, and it doesn’t increase the cost and only increases profits.
External Economies of Scale
Ideally the entire industry enjoys this kind of economies. The external economies of scale come up when the scope of operations of the industry increase due to exterior developments.
For instance, the creation of better transport might lead to a significant reduction in both the cost of the company and industry overall.
Under the external economies of scale, almost all the companies in the industry benefit.
Impact of Economies of Scale on Cost of Production
At any stage, a company can realize the economies of scale. Here the term production is all about the economic concept of the show, and it features all the activities with regards to commodity.
It doesn’t include the final consumer. Hence a company can choose to implement economies of scale in the marketing department by hiring marketing experts.
On the flip side, the company can also hire professionals in the input sourcing division. They can move from human labor to machine labor.
Production Costs Effects
- It minimizes the fixed cost of production. Additionally, it is due to an increase in output as fixed cost spreads over a large part of the production.
- It also minimizes the per-unit variable costs. The same takes place due to the expanded production scale, which increases the production process’s efficiency.
What are Diseconomies of Scale?
Just like economies of scale, even the diseconomies of scale take place.
To begin with, one needs to know that at times a company chases economies way too much because of which it becomes enormous.
The overgrowth is basically known as diseconomies of scale. The economies of scale are entirely opposite to diseconomies of scale.
In simple terms, when long-run costs increase with an increase in the price of production, the companies tend to become way less efficient.
When the company is too huge, the communication within the company is also less, which might lead to slower decision making and less responsiveness.
The business makes business less lucrative as there is a lack of flexibility.
Difference between Internal & External Economies of Scale
The internal economies of scale take place when the company minimizes the cost internally, so it is specific to a common part.
Huge companies quickly achieve economies of scale by reducing their costs and increasing their production level. It is mainly because they can buy in bulk and have some patents also.
On the flip side, the external economies occur because of the factors prevailing in the entire industry.
Hence, no one company controls the production cost on its own. It can be anything from tax reductions, subsidies, high skilled labor pool, etc.
Comparing the Economies of Scale and Economies of Scope
One needs to understand the differences between the two firms. No doubt, both the terms describe the changes in long-term average costs.
The difference mainly takes place when there is a shift in the type of changes. By now, you must be knowing that economies of scale take place due to more significant production volumes.
On the flip side, the economies of scope take place due to a great variety of products.
It is quite different because economies of scale don’t depend on the variety of products, and the cost per unit reduces to an increase in the level of production.
Above all, one just needs to mass produce for the economies of scale to take place.
When compared to economies of scope, they need multiple product types to increase efficiency overall and minimize the cost of production.
Is it truly worth it?
There is a global debate about the effects of the expansion of scale, and then it turns to international trade and globalization of the economy.
The balance between demand and supply tends to become weaker as businesses tend to become more significant.
Economies of Scale – Conclusion
The sources tend to vary when it comes to understanding economies of scale and diseconomies of scale.
Economies of scale are basically cost advantages that a company experiences when its production becomes efficient.
Open Demat Account Now! – Zero Brokerage on Delivery
Most Read Articles
